George Borst
Business Development Lead
August 05, 2024
IThe process industry is known for its complexity, handling everything from intricate chemical reactions to vast mechanical systems. However, as the industry evolves, it faces significant challenges, including a shortage of skilled workers, rigid automation systems, and the need for extensive data collection. Simplification emerges as a powerful solution to these challenges, offering a way to streamline operations, reduce the burden on workers, and enhance overall efficiency.
In this blog, we will explore the importance of simplification in the process industry, the impact it can have on operations, and effective strategies to achieve it. Simplification not only makes processes easier to manage but also paves the way for better data utilization, proactive maintenance, and flexible team roles, ultimately transforming how the industry operates.
Key Challenges in the Process Industry
The process industry is complex. It deals with many challenges, from physical constraints to standardizing automation processes. For plant managers, maintenance managers, automation managers and process engineers, understanding these complexities is crucial for efficient and reliable operations.
1. Increasing Demands and Skilled Labor Shortage
The process industry is always advancing to solve operational problems at hand. However, there is a shortage of skilled workers. This puts a lot of pressure on existing staff to meet growing demands and fix problems quickly to avoid downtime.
2. Rigid Automation Systems
Traditional automation systems are designed to be reliable, safe, and accurate but often lack flexibility. This makes it difficult to digitalize processes within the existing automation framework.
3. Building and Managing Control Loops
Control loops are crucial in the process industry. They are used in handling raw materials, processing equipment, safety systems, and packaging and storage. Creating these control loops involves selecting and integrating instruments, valves, pumps, and other equipment into piping systems. After integration, these components must be connected to a control system that uses algorithms to ensure the correct process values for the desired end product.
4. Specialized Knowledge and Maintenance
Operating advanced equipment requires specialized knowledge. Each piece of equipment has its own maintenance needs and potential points of failure, which need to be monitored continuously. As more equipment is added to gather process data, the need for specialized knowledge increases, creating additional maintenance points and complexities.
5. Data Collection and Optimization Challenges
To optimize plant operations, reduce costs, predict maintenance needs, and improve efficiency, more equipment is needed to gather both process and equipment data. However, traditional automation systems are not flexible or built to easily gather extensive data.
This means choices must be made to optimize parts of the plant with the most impact on operational costs and downtime, often overlooking optimization at the field or control level.

The Need for Simplification in the Process Industry
Simplification is essential to address the challenges of the process industry. By making processes and equipment simpler, it becomes easier to achieve optimization and more efficient operations. Simplified systems require less specialized knowledge, reducing the burden on skilled workers and making maintenance easier. This approach allows for easier access to optimization opportunities and more time to focus on improving plant performance.
Impact of Simplification
Simplification can transform the process industry by making it more adaptable and responsive to changes. It enables better data collection and analysis, leading to more informed decision-making and proactive maintenance strategies. Ultimately, simplification can lead to significant improvements in efficiency, cost reduction, and overall plant performance, helping to overcome the complexities that have long been part of the process industry.
Advantages of Process Simplification
Simplification is crucial in the process industry for optimizing operations and ensuring efficiency. By simplifying processes and equipment, plants can become more efficient and manageable, even with fewer skilled workers.
Enhanced Workforce Understanding
Simplified processes help everyone, from management to field workers, understand plant operations better. Generalists can replace specialists, making it easier to manage the plant with less specific training.
Instant Health Status
A simplified system allows quick access to the health status of equipment and processes. This helps identify urgent issues, preventing process stops and enabling timely interventions.
Efficiency and Data Sharing
Simplified systems help spot efficiency improvements and share data easily with third parties, enhancing the plant’s reliability and performance.
Flexible Team Roles
With simplified equipment, team members can easily take over each other’s tasks, ensuring smooth operations even when specific members are unavailable.
In summary, simplification is key to optimizing operations in the process industry. It improves workforce flexibility, understanding of plant operations, and the ability to make timely interventions, leading to significant gains in efficiency and reliability.

Strategies for Simplification
Simplifying processes in the process industry involves using the right strategies to make equipment and workflows more efficient and user-friendly. Here are some key strategies to achieve simplification:
1. User-Friendly Equipment
Start with equipment that is easy to use. This helps users quickly understand how to configure the equipment and make necessary interventions. Consider using equipment with apps or interfaces that can connect to smart devices, as most people are familiar with using these devices daily.
2. Integrated and Efficient Equipment
Using less equipment that gathers more data ensures more standardization, fewer leak points, and fewer points of failure. Look for integrated equipment that provides more value with less effort. This also reduces the amount of work needed to make the equipment work seamlessly together. When equipment is designed to work together, it results in better outcomes and improved process efficiency.
3. Built-In Analysis
Analyzing data can be challenging. Equipment with built-in analysis capabilities can provide immediate health status without requiring users to be data or component experts. Equipment with embedded computers or edge solutions can offer direct health assessments and generate asset health status reports that can be downloaded or sent automatically.
4. Digital Twins
Using equipment that utilizes digital twins allows you to focus on the bigger picture. Digital twins ensure that equipment continues to operate even when there are minor issues, giving you more time to keep processes running smoothly and plan maintenance during appropriate times.
5. AI on the Field Level
Implement AI at the field level to identify deviations and opportunities for improvement. Equipment with computing power or Ethernet-based connections can gather more data and send valuable information to a centralized environment, helping to optimize operations.
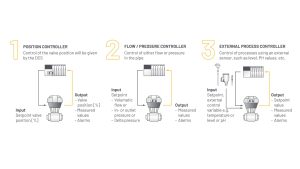
Example: Smart Meter Valves
An example of simplifying process control is using smart meter valves for flow control, pressure control, or external sensor control in utility processes. These devices make it easier to build control loops for flow, pressure, level, or temperature control, enhancing overall process efficiency.
By adopting these strategies, the process industry can achieve significant simplification, making it easier for workers to manage equipment and processes, improving efficiency, and reducing downtime.

Do you want to see a practical example?
Watch the video below to see how FOCUS-1 is used in a waste incineration plant!
Conclusion
Simplification is crucial for the process industry’s evolution, offering solutions to complex challenges like workforce shortages and rigid automation systems. By simplifying processes and equipment, organizations empower generalists to manage operations effectively and make informed decisions based on improved data utilization. This approach not only enhances operational efficiency but also reduces costs, enhances reliability, and improves overall plant performance.
Embracing user-friendly equipment, integrated systems, built-in analysis, digital twins, and AI-driven solutions is essential. These innovations enable adaptability to changing demands and facilitate continuous improvement. Simplification isn’t just about making things easier—it’s about unlocking new potentials, optimizing resources, and ensuring sustainable growth in a dynamic global landscape. Let simplification drive efficiency, innovation, and success in the future of the process industry.
Ready to Simplify Your Operations?
Other blogs that might interest you:

How in Steel Production Smart Meter Valves Reduce Downtime
Discover how ArcelorMittal uses FOCUS-1 smart meter valves to improve flow control, reduce downtime, and detect faults faster in steel production.
The new way of process control with FOCUS-1 in automation
Read about how the FOCUS-1 replaces valves, sensors, and controllers with one smart device while cutting complexity, boosting efficiency, and enabling real-time process control.

How FOCUS-1 saves space, time & energy in process automation
Discover how FOCUS-1 saves space, time & energy by combining flow, pressure, and control functions into one smart device. Simpler setup, better performance.

FOCUS-1 vs. traditional control loops: What’s the difference?
Find out how FOCUS-1 transforms process automation by replacing traditional control loops with an all-in-one smart device. Simplify operations, cut costs, and enhance efficiency with integrated flow, pressure, and temperature control.

FOCUS-1 explained: How this all-in-one smart meter valve replaces traditional control systems
FOCUS-1 is transforming process automation by replacing traditional control systems with an all-in-one smart device. This blog breaks down how it integrates measurement, control, and computing to simplify operations, reduce costs, and enhance efficiency.

How Nobian Tested FOCUS-1’s Functionalities: Precision & Efficiency for Industry 4.0
Discover how Nobian tested the FOCUS-1 Smart Meter Valve, unlocking new levels of precision and efficiency in their operations.